Pirelli Position
Pirelli, in compliance with stringent quality control procedures, welcomes and fully supports the introduction of the tyre label, considering it an excellent means to offering end-users more transparency and help in obtaining information when purchasing new tyres. The overall value of a tyre must be measured on a full list of factors (handling both on dry and wet surfaces, aquaplaning behaviour, high speed stability, dry braking, mileage etc.) on which Pirelli tests all tyres.nAs the label doesn’t show certain more specific information about a particular tyre such as winter tyres and their performances, the dealers retain a crucial role in the consumers purchasing decision as they will always be the expert who can recommend the right tyre for the individual needs of each end user.







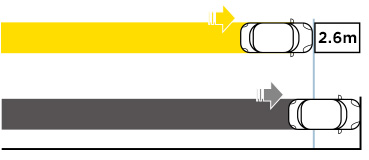 *Tüv Süd Automotive, tyre test report n° 76247671 year 2011 (ref. Pirelli tyres - size 225/50 zr17)
*Tüv Süd Automotive, tyre test report n° 76247671 year 2011 (ref. Pirelli tyres - size 225/50 zr17)